The Earth is in a critical situation for human beings. The environmental problems are “a matter of life.”
As scientists from all over the world have proven, the changes in the Earth due to global warming are unstoppable, and as we call it the climate crisis, it is an urgent issue for the entire planet.
Since 1979, when satellite observations began, Antarctic ice has been melting at a rate of 13.3% per decade, and it has been reported that since 2002, 286 gigatons of ice on land have been lost every year, and the world’s sea level has risen by 17.8 centimeters in the last 100 years.
While I was visiting the Philippines when I was a student, I saw garbage buried in clean sandy beaches because of the lack of a garbage collection system, powerful typhoons causing damage, and food harvests decreasing because of the impact of the environment. Upon witnessing these changes on the Earth, which I had never experienced in Japan, I realized that the environmental issues I had been learning in the classroom were “a matter of life,” which had already resulted in irreversible changes.
1World’s average surface temperature at a record high
According to an announcement by the National Aeronautics and Space Administration (NASA) and the National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration (NOAA) on January 14, 2021, the global average surface temperature in 2020 was the second-highest on record after 2016, which was the highest on record since observations began in 1880. This marked the second-highest temperature after 2016, which broke the record for the third consecutive year since 2014, and there are concerns that the warming trend will continue for a long time.
After NASA and NOAA analyzed temperature data collected at some 26,000 observation facilities around the world and by ships and other means at thousands of locations in the ocean, they found that the average temperature for the past 20 years was 14.88 degrees Celsius, nearly 1 degree Celsius higher than the 20th century’s average of 13.90 degrees Celsius.
The CO2 concentration and the temperature are closely related. Now that the CO2 concentration in the atmosphere has exceeded 400ppm (a 40% increase compared to the pre-industrial era), it is said that the Earth is obviously getting warmer compared to the past.
2Japan’s responsibility as the world’s fifth-largest CO2 emissions source
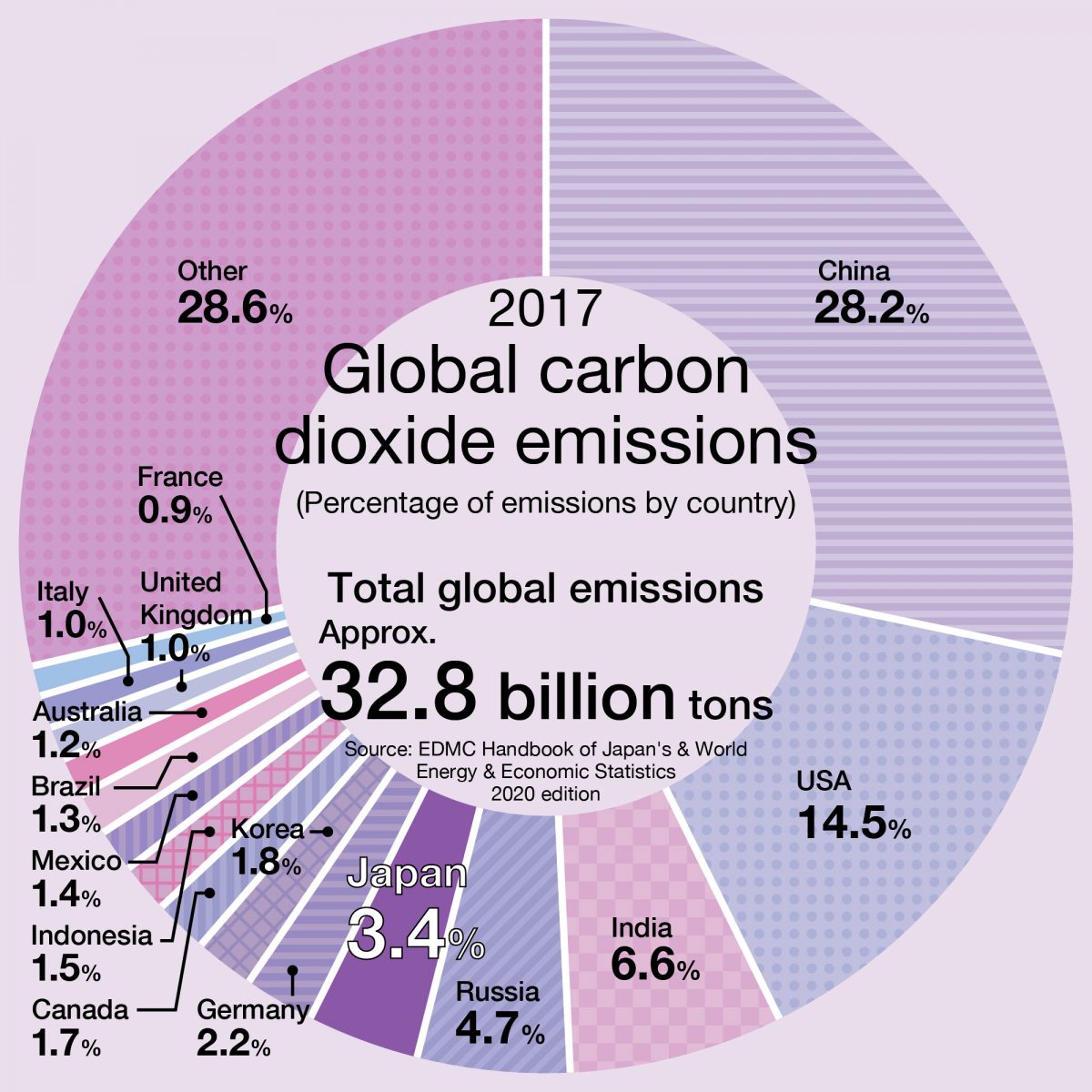
According to the EDMC/Energy and Economic Statistics Handbook 2020, global CO2 emissions in 2017 were approximately 32.8 billion tons, with China being the country with the largest amount of CO2 emissions, followed by the United States, India, Russia, and Japan. China emits about 9 billion tons every year, the U.S. about 5 billion tons, India about 2 billion tons, Russia about 1.5 billion tons, and Japan about 1.1 billion tons.
Among the top five CO2 emission countries, the U.S. has the highest per-capita emissions (per year) of about 14.6 tons, followed by Russia with the second-highest per-capita emissions of about 10.6 tons, and Japan with the third-highest per-capita emissions of about 8.9 tons.
97% of scientific papers on the subject of global warming assumes that the CO2 increase from human activities is primarily responsible for global warming, and more than three-quarters of the increase in atmospheric CO2 concentration over the past 20 years is said to be attributable to the burning of fossil fuels, such as coal and oil.
In order to reduce the CO2 concentration and slow down the excessive global warming, we are required to reduce the use of fossil fuels such as coal and oil, and we may need to fundamentally review our current social structure and lifestyle.
Designing a society that can reduce CO2 levels and minimize global change is needed.